Net-SNMP
Net-SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) includes an open source SNMPd agent to monitor and administer SNMP capable network devices like routers and switches.
You can poll the snmpd agent on the router to obtain e.g. interface or CPU statistics information and display this in a nice graph with the help of a program like MRTG
More info about Net-SNMP can be found via: http://www.net-snmp.org/
Creating a Feetz Image with Net-SNMP
Follow the directions from the Wiki
After the following step you can configure the packages you want to have included in your image.
make menuconfig
Make sure the following is selected (so I have 1 out of 3 selected):
Package selection ---> Standard packages ---> [*] Net-SNMP 5.4.2.1 snmpd Package selection ---> Standard packages ---> [ ] With openssl encryption (NEW) Package selection ---> Standard packages ---> [ ] With zlib compression (NEW)
Setup in Freetz web-interface
conf
First you should create a snmpd.conf file. This file contains all configuration options for Net-SNMP, including a community string, which you can regard as a password for access control. [[br]
A full description of all possible parameters can be found in the online manual page: http://www.net-snmp.org/docs/man/snmpd.conf.html
You can edit the snmpd.conf file via the Freetz web-interface via Net-SNMP > snmpd.conf
If you would like to have a minimal config you can use the following:
rocommunity public rwcommunity private
This way access contol is only based on the communiy string.
I found an example config with more accss contol options in one of the attachments in this thread: http://www.ip-phone-forum.de/showthread.php?t=122073
This shows how to control access based on source IP address range with additional options to restrict access.
## sec.name source community ## ======== ====== ========= com2sec readonly 127.0.0.0/8 <community string> com2sec readonly 192.168.0.0/16 <community string> #com2sec paranoid default <community string> com2sec paranoid 172.16.0.0/16 <community string> ## Access.group.name sec.model sec.name ## ================= ========= ======== group MyROSystem v1 paranoid group MyROSystem v2c paranoid group MyROSystem usm paranoid group MyROGroup v1 readonly group MyROGroup v2c readonly group MyROGroup usm readonly ## MIB.view.name incl/excl MIB.subtree mask ## ============== ========= =========== ==== view all included .1 80 view system included .1.3.6.1.2.1.1 ## MIB ## group.name context sec.model sec.level prefix read write notif ## ========== ======= ========= ========= ====== ==== ===== ===== access MyROSystem "" any noauth exact system none none access MyROGroup "" any noauth exact all none none
If you only allow access from inside your trusted network you can use the default community string, which is for readonly public and for readwrite private.
More information on the View-Based Access Control Model (VACM) can be found on the Net-SNMP Wiki
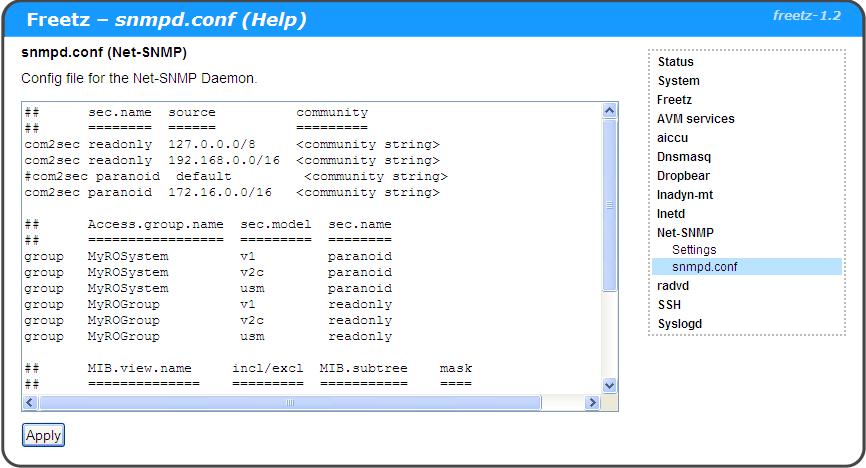
setup
After saving a snmpd.conf file using the Net-SNMP > snmpd.conf setup page you can enable Net-SNMP to start automatically at bootup.
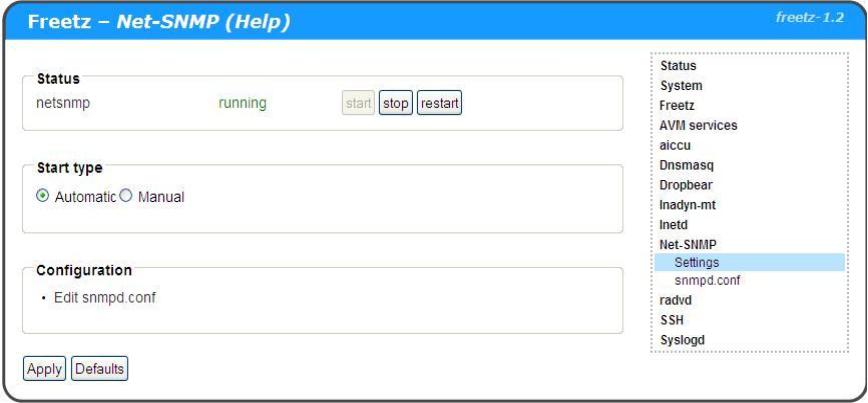
verify
With many Linux distributions you als have snmp tools included like snmpget, snmpset, snmpwalk, …
A quick guide how to use these tools can be found on the net-snmp.org site.
Some commands: To get a list of interface descriptions (ifDesc):
snmpwalk -v 2c -c <community string> 192.168.178.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2
snmpwalk -v 2c -c <community string> -O a 192.168.178.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2
To get a list of all available objects:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c <community string> 192.168.178.1 .1
MRTG
The Multi Router Traffic Grapher will allow you to generate nice graphs of the data available via SNMP.
This can be system information like uptime, interface information and statistics, and more.
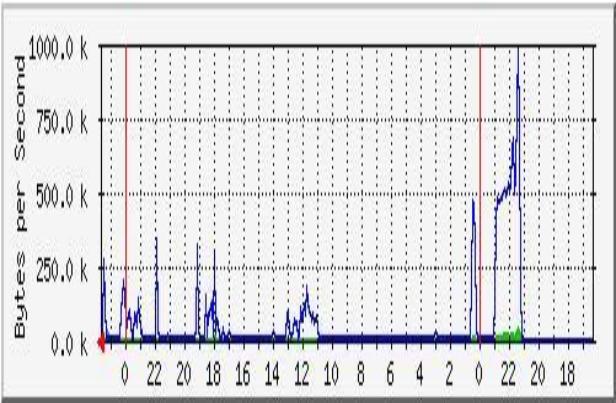
The graphs can help a lot with trouble clearing issues, both with the FritsBox (e.g. CPU memory), and in the network.
For more info see the MRTG site.
Here an example on the graph you can generate:
The following wiki page will provide more detailed information to installation and configuration:
